Muons (WP17)
Coordinator: Stephen Cottrell, ISIS/STFC
Objectives
Muon spectroscopy is a powerful way of studying atomic level properties of matter, often producing complementary results to neutron scattering. Europe is fortunate in having two muon sources, ISIS in the UK and PSI in Switzerland, which each provide different facilities for muon experiments.
The aim of this JRA is to develop technologies and techniques which extend the range of capabilities of the muon method available to European users at these two facilities.
To learn about the last developments of this JRA read the Muons' JRA last update here.
 What are muons?
What are muons?
Watch ISIS scientists Philip King and Adrian Hillier explain what muons are and how they are produced at ISIS.
 JRA series - Elvezio Morenzoni
JRA series - Elvezio Morenzoni
Watch Elvezio Morenzoni from the PSI Muon spin spectroscopy lab describe their work as part of the Muon Joint Research Activity.
 Muon JRA - ISIS
Muon JRA - ISIS
James Lord describes Hifi, the high-field muon spectrometer developed as part of the JRA, at ISIS.
 Muon JRA - ISIS
Muon JRA - ISIS
Peter Baker, scientists at ISIS, describes recent work carried out on HiFi.
Muon JRA picture gallery

Muon instrument HiFi@ ISIS
The new high-field muon spectrometer (HiFi) at ISIS provides magnetic fields up to 5T for muon studies of magnetism, molecular dynamics and polymer systems. Computer simulations of muon and positron paths through the instrument were undertaken with NMI3 JRA funding to enable the instrument detector array to be designed. The instrument is working very successfully as a full part of the ISIS user programme.
Picture: Stephen Kill, ISIS

SmuS
SμS high field spectrometer, PSI.
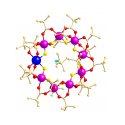
Figure 3 a
The first example of an energy level crossing in a molecular nanomagnet detected with muons (Lancaster et al, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 2011 23 242201).
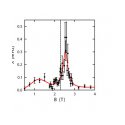
Figure 3 b
The first example of an energy level crossing in a molecular nanomagnet detected with muons (Lancaster et al, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 2011 23 242201).
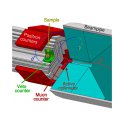
Figure 4

Figure 5 a

Figure 5 b
A prototype detector module based on avalanche photodiodes developed at the SμS.

Figure 6 a
Gas target pressure cell designed for the ISIS high field spectrometer – see Figure 6 b for an avoided level crossing measurement of the Mu-ethyl radical formed by implanting muons in ethene gas at 300K.
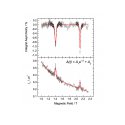
Figure 6 b
Avoided level crossing measurement of the Mu-ethyl radical formed by implanting muons in ethene gas at 300K.












