Neutron Optics (W17)
Coordinator: Fréderic Ott, LLB/CEA
Objectives
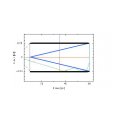
The main aims of this Joint Research Activity have been to develop neutron optics technology for high flux reflectometry, using super-mirrors, as well as the development of new focusing optics devices. More information about the specific tasks is available here.
Each thematic task gathers instrument scientists who are experts in their fields (reflectometry, SANS , diffraction or imaging) and who have a direct interest in improving their spectrometers. Most of the proposed developments are being implemented on existing spectrometers and will benefit the wider neutron community.
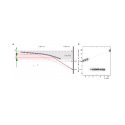
Most of the optics developments require advanced numerical simulations. Monte-Carlo simulation programs have been upgraded or rewritten to include new advanced components and optimization tools. This will also be of benefit to a wide community.
Please see this page for the last technical update. Watch the video below for more information about the work carried out at HZB.
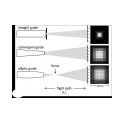
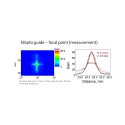
Nikolay Kardjilov talks about the work carried out at the Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin on elliptic focusing guides.The pictures below provide more information.
Neutron Optics Picture gallery